What is Column?
- We knew that in a framed structure A vertical structural member which can transmit the load from the slab, beam along with its self-weight to the foundation is called column.
- Why we provide column?
- Columns carry axial loads and therefore are designed for compression.
- Other loads from snow, wind or other horizontal forces can cause bending in the columns.
- We shall build up a small size structure by RR masonry at a certain height but the multi-story building cannot be constructed by RR masonry because the structure can able to transmit the heavy load to the foundation.
- Basically, a column designed to distribute the compressive axial load & additional forces like snow, wind to the foundation eventually & it could be sustained the structure even in the earthquake or any other force majeure.
- Column- Based on Shape & Reinforcement
- Square/Rectangular Column
- Composite/Encased Column
- Circular Column
- Y Type Column
- T Type Column
- L Type Column
Square/Rectangular Column
- Most of the building structure was constructed by square or rectangular column. Significantly both are having same components and it is differ based on its architect view.
- These type of column was economically good and easy to do shuttering, placing reinforcement & Concrete.
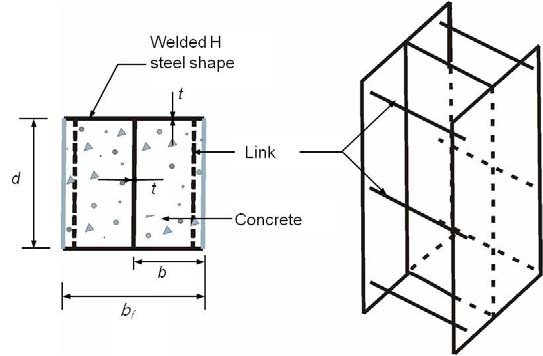
- Composite/Encased Column
- A vertical structural element, with a combination of steel section & concrete it is called as encased or composite column.
- The composite column mostly provided for truss structure to avoid the steel corroded by any type of chemical.
Circular Column
- The bending resistant is higher than square/rectangular column.
- It occupies the lesser area.
- Square/rectangular column reinforcement minimum 4 nos of steel will be places in the corner but in a circular column provide more than 4 nos.
- Mostly in building circular column provided for the aesthetic purpose.
- Economically it is little high to compare to square or rectangular column.
- Y-type Column
- These type of column mostly using for bridges construction.
- The design of bridges to sustain the dead load of the structure & live load of the vehicle motion, the load was eventually distributed to the column.
- T-type Column
- These type of column having same features like square/Rectangular type column.
- Mostly it was provided along with retaining wall or boundary wall based on design requirement.
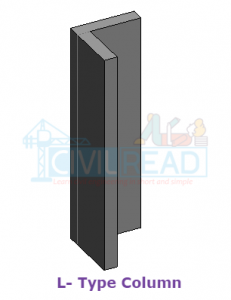
- L-type Column
- The L type column has used in boundary wall construction and heavy type L column was used in the turning of metro rail or bridges construction.
Column- Based on Load
- Axial Load Column
- Uniaxial Load Column
- Bi-Axial Load Column
- Eccentric Load Column
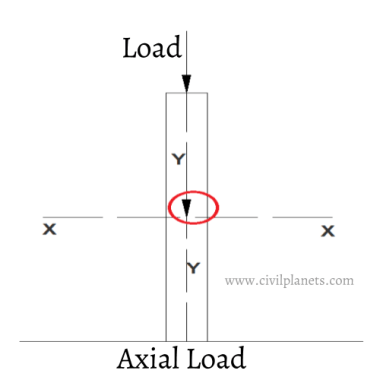
Axial Load Column
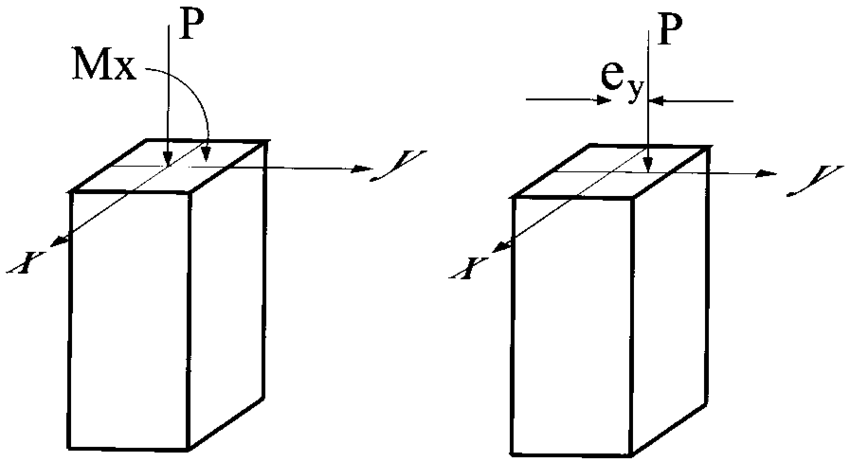
- The entire load passes through the centre axis of the column which coincides with the X-axis, it is called Axial Load.
- The load shall be either compression or tensile load.
Uniaxial Load Column
- The eccentric load act on either X axis or Y axis it is called Uni axial load column.
Bi-Axial Load Column
- The eccentric load act on either X axis or Y axis it is called Uni axial load column.
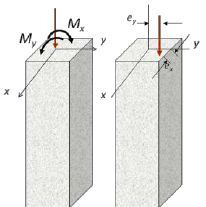
Eccentric Load Column
- The load shall pass parallel to the centre axis of the member but act on its cross-section that’s called Eccentric load.
Column- Based on Slenderness Ratio
- The length of the column divided by its radius of gyration, it is called slenderness ratio of the column.
- The slenderness ratio is used to find out the buckling stress of the column.
- Long Column
- Short Column
Long Column
- Slenderness ratio of the column is greater than 12 it is called long column.
- The column may fail on both compression & buckling load.
Short Column
- Slenderness ratio of the column is less than 12 it is called short column.
- The sort column may fail by compression stress.
-

short column and long column